SA JOURNAL OF DIABETES & VASCULAR DISEASE
RESEARCH ARTICLE
VOLUME 14 NUMBER 1 • JULY 2017
27
improve vasorelaxation to acetyl choline in the aorta of diabetic
rats.
10,24
Majithiya and colleagues reported that treatment with
pioglitazone reduced blood pressure, reduced oxidative stress and
restored endothelial function in STZ-induced diabetic rats. The fact
that pioglitazone reduced oxidative stress may have been a cause
of the reduction in blood pressure.
The protective effect of pioglitazone against oxidative stress
may prevent the breakdown of NO, which may improve vascular
function. Similar observations were made by Bagi and co-workers
that pioglitazone increased NO bio-availability and reduced
oxidative stress in coronary arterioles of mice with type 2 diabetes.
25
Matsumoto and colleagues reported that chronic treatment with
pioglitazone restored impaired NO-mediated, endothelium-
dependent relaxation in diabetic rat aortae.
26
It has been shown
that reduction in blood pressure in the case of STZ-induced diabetic
rats was NO mediated.
4
Calnek and co-workers reported that PPAR-
gamma agonists increased NO bioavailability in cultured cells.
27
Pioglitazone was shown to directly induce a relaxation of rat
aortae pre-contracted with phenylephrine, which was inhibited by
L-NAME.
10
Similarly, indomethacin-treated vessels incubated with
pioglitazone markedly reduced the phenylephrine contractions.
3
Although most researchers agree that the sensitivity to phenylephrine
was unchanged during the early stage of diabetes (up to 12 weeks
in STZ-induced diabetic rats), they disagree on the response to
phenylephrine. Agrawal and McNeill reported an increase in
contractility in response to phenylephrine,
28
Pfaffman and co-workers
reported a decrease,
29
and Scarborough and Carrier and White and
Carrier reported no change.
30,31
In contrast, studies that extended the
diabetic duration up to 43–52 weeks have demonstrated a consistent
increase in sensitivity to noradrenaline in rat aortae
32
and mesenteric
arteries
33
from STZ-induced diabetic rats.
In our study, we suggest that our diabetic rats did not have
enough time to develop a sufficiently severe degree of vascular
dysfunction to manifest an effect to phenylephrine. From our results,
acute pioglitazone/losartan pre-treatment did not significantly
change the maximum contractile responses to phenylephrine in the
control, diabetic or hypertensive rats.
We attempted to determine whether these drugs affected the
endothelial modulatory responses to vasoconstriction produced
by phenylephrine. Sensitivity of the aortic rings to phenylephrine
was decreased in the presence of pioglitazone and/or losartan.
The glitazones have been shown by Asano
et al
. to decrease
smooth muscle cell contractility,
34
and by Dormandy
et al
. to cause
improvement in vascular function.
35
We believe, however, that the
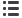
Figure 5.
Effects of pioglitazone and losartan on the response of aortic segments
to increasing concentrations of clonidine in the control group. Cont: control,
Pio: pioglitazone, Los: losartan, Pio+Los: pioglitazone + losartan. Values are
expressed as mean ± SEM (
n
= 14). *Cont vs Pio (
p
= 0.001); *Cont vs Los (
p
=
0.011); #Cont vs Pio+Los (
p
< 0.001).
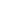
Figure 6.
Effects of pioglitazone and losartan on the response of aortic segments
to increasing concentrations of clonidine in the HT group. Cont: control, Pio:
pioglitazone, Los: losartan, Pio+Los: pioglitazone + losartan. Values are expressed
as mean ± SEM (
n
= 5). *Cont vs Pio (
p
= 0.004); *Cont Clo vs Los (
p
= 0.014);
*Cont Clo vs Pio+Los (
p
= 0.001).
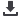
Figure 7.
Effects of pioglitazone and losartan on the response of aortic segments
to increasing concentrations of clonidine in DM group. Cont: control, Pio:
pioglitazone, Los: losartan, Pio+Los: pioglitazone + losartan. Values are expressed
as mean ± SEM (
n
= 16). *Cont vs Pio+Los (
p
= 0.005).
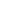
Figure 8.
Effects of pioglitazone and losartan on the response of aortic segments
to increasing concentrations of clonidine in the HT + DM group. Cont: control,
Pio: pioglitazone, Los: losartan, Pio+Los: pioglitazone + losartan. Values are
expressed as mean ± SEM (
n
= 13).