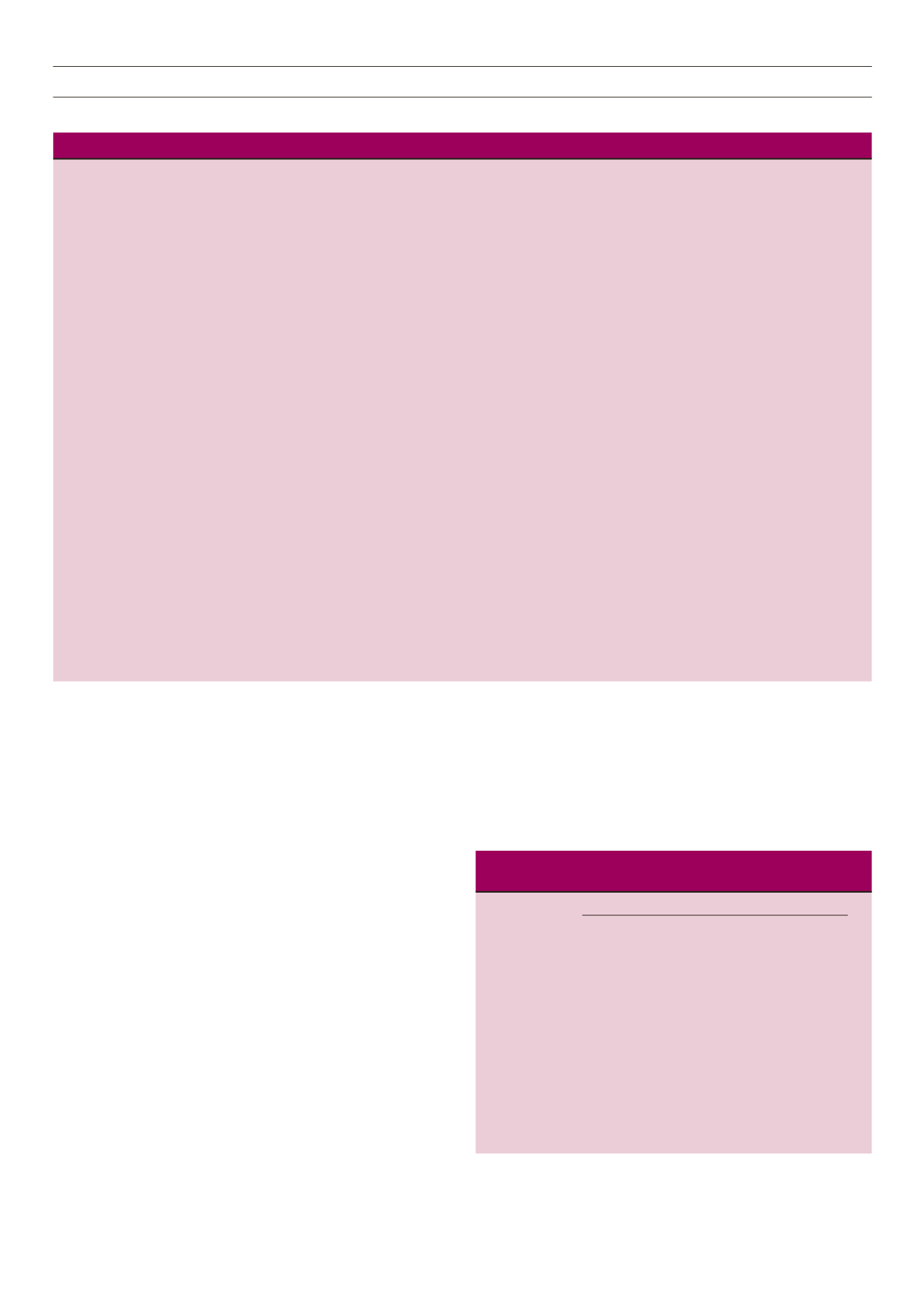
RESEARCH ARTICLE
SA JOURNAL OF DIABETES & VASCULAR DISEASE
74
VOLUME 16 NUMBER 2 • NOVEMBER 2019
the lowest levels of SBP, DBP, HR and PP. It also had the lowest
prevalence of hypertension and pre-hypertension (Table 4).
Boys and girls were separated into lean and overweight/
obese groups using selected measures of adiposity. BMI < 85th
percentile was classified as lean and BMI ≥ 85th percentile as
overweight/obese. WC, TFM and WHtR were separated into
two groups: ≤ 75th percentile for gender was classified as lean
while > 75th percentile was classified as overweight/obese. A
greater WC conferred a 1.7-times greater risk of developing
hypertension (
p
= 0.008) in the cohort. The relative risk of having
hypertension conferred by high BMI, WC, WHtR and TFM was
absent in boys but weak and not significant in girls (Table 5).
Discussion
In this study we showed that the prevalence of overweight and
obesity in 10- to 14-year-old children in the Eastern Cape was
over 10 and 14%, respectively, while the prevalence of pre-
hypertension and hypertension were 12 and 20%, respectively.
Gender-specific analysis showed that the girls were more obese
and also had a higher prevalence of hypertension and pre-
hypertension. Although the relative risk of having hypertension
with increasing adiposity was small, children whose BMI,
WC, TFM and WHtR were higher than the third quartile had
significantly (
p
< 0.05) higher blood pressure than those in the
lower quartiles.
Using all four selected measures of adiposity (BMI, WC, TFM
and WHtR) our study showed that girls were larger and had a
higher prevalence of overweight and obesity. Participants in this
study were 10 to 14 years old, which is a period of much hormonal
activity. Puberty begins in girls from eight to 12 years old, while
in boys it begins from nine to 14 years old. This period in girls
Table 4.
Components of blood pressure in the four quartiles of BMI, WC, TFM and WHtR
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
Parameters
quartile
quartile
quartile
quartile
p
-value
BMI
SBP (mmHg)
107.1 ± 1.5
110.4 ± 0.5
113.9 ± 1.0**
117.3 ± 1.1**
##
0.0001
DBP (mmHg)
69.1 ± 1.1
71.8 ± 0.4
73.4 ± 0.8*
73.3 ± 0.9*
0.03
HR (beats/min)
87.9 ± 1.9
87.3 ± 0.7
84.9 ± 1.6
89.3 ± 1.3
0.14
PP (mmHg)
38.1 ± 1.3
38.7 ± 0.4
40.4 ± 0.9
##
44.1 ± 0.9
##
0.0001
HT,
n
(%)
3 (8.8)
59 (16.1)
14 (23.7)
13 (16.5)
preHT,
n
(%)
9 (26.5)
125 (34.2)
23 (39.0)
34 (44.7)
TFM
SBP (mmHg)
108.8 ± 0.9
110.2 ± 0.9
112.2 ± 0.9**
114.9 ± 0.8**
##
0.0001
DBP (mmHg)
70.6 ± 0.7
71.7 ± 0.7
72.4 ± 0.9
73.0 ± 0.6
0.14
HR (beats/min)
87.5 ± 1.1
86.1 ± 1.1
88.5 ± 1.2
87.7 ± 1.0
0.50
PP (mmHg)
38.2 ± 0.7
38.5 ± 0.7
39.8 ± 0.7
42.0 ± 0.7**
##
0.0001
HT,
n
(%)
17 (12.8)
20 (14.8)
23 (11.8)
28 (20.1)
preHT,
n
(%)
37 (27.8)
46 (34.1)
48 (24.6)
58 (43.6)
WC
SBP (mmHg)
108.1 ± 0.8
109.8 ± 0.9
112.3 ± 1.1**
115.8 ± 0.7**
##
0.0001
DBP (mmHg)
70.9 ± 0.6
71.2 ± 0.7
71.7 ± 0.7*
73.7 ± 0.6*
0.05
HR (beats/min)
86.8 ± 1.1
87.6 ± 1.1
87.1 ± 1.2
89.3 ± 1.3
0.78
PP (mmHg)
37.2 ± 0.6
38.6 ± 0.7
40.7 ± 0.9
##
42.1 ± 0.6
##
0.001
HT,
n
(%)
25 (16.7)
27 (18.9)
19 (20.4)
46 (29.7)
preHT,
n
(%)
49 (32.9)
44 (30.8)
31 (33.3)
69 (44.5)
WHtR
SBP (mmHg)
109.0 ± 0.9
111.1 ± 0.9
110.6 ± 0.9
115.4 ± 0.8***
##$$$
0.0001
DBP (mmHg)
71.0 ± 0.7
72.3 ± 0.7
71.0 ± 0.6
73.3 ± 0.6*
$
0.05
HR (beats/min)
86.9 ± 1.1
87.1 ± 1.2
88.1 ± 1.1
87.3 ± 1.0
0.75
PP (mmHg)
37.9 ± 0.6
38.8 ± 0.7
39.6 ± 0.7
42.1±0.7***
###$
0.0001
HT,
n
(%)
19 (14.1)
26 (19.3)
28 (20.6)
40 (30.1)
preHT,
n
(%)
37 (27.4)
54 (40)
42 (30.9)
59 (44.4)
BMI: body mass index, WC: waist circumference, TFM: total fat mass, WHtR: waist-to-height ratio, HT: hypertension; preHT: pre-hypertension, SBP: systolic
blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure, HR: heart rate, PP: pulse pressure.
*Compared to first quartile (*
p
< 0.05, **
p
< 0.01, ***
p
< 0.001),
#
compared to second quartile (
#
p
< 0.05,
##
p
< 0.01,
###
p
< 0.001) and
$
comparing quartile 4 to
quartile 3 (
$
p
< 0.05,
$$
p
< 0.01;
$$$
p
< 0.001).
Table 5.
Relative risk of having hypertension with high measures of adi-
posity
Relative risk
Variables
Cohort
Males
Females
BMI
1.04
1.05
1.28
95% CI
0.544–1.975
0.652–1.716
0.974–1.675
p
-value
0.86
0.862
0.090
WC
1.71
1.203
1.328
95% CI
1.284–2.279
0.774–1.870
1.003–1.758
p
-value
0.0008
0.418
0.06
TFM
1.42
0.859
1.384
95% CI
0.891–2.00
0.539–1.370
0.877–1.558
p
-value
0.183
0.542
0.189
WHtR
1.27
1.245
1.26
95% CI
0.766–2.119
0.790–1.961
0.956–1.671
p
-value
0.351
0.385
0.133
BMI: body mass index, WC: waist circumference, TFM: total fat mass, WHtR:
waist-to-height ratio, CI: confidence interval.