SA JOURNAL OF DIABETES & VASCULAR DISEASE
RESEARCH ARTICLE
VOLUME 17 NUMBER 1 • JULY 2020
19
with findings by Owalabi
et al
.,
46
which revealed that 49.2% of
the Buffalo City metropolitan municipality adults had a high
prevalence of hypertension. The findings of the study are also
lower when compared to a study by Day
et al
.,
47
which reported
a 40% prevalence of hypertension among adults in South African
provinces during 2010. Peer
et al
.
48
also reported a lower prevalence
of hypertension (38.9%) among black urban South African adults
between the ages of 24 and 65 years in Cape Town.
The study showed that women (27%) had a higher prevalence
of hypertension compared to males (22%). This is lower than the
study by Ntuli
et al
.
49
in adults in a rural community of Dikgale in
the Limpopo Province, which showed that 42% of males and 41%
of females were hypertensive.
The findings of our study are also similar to those of the South
Africa Demographic and Health Survey (SADHS),
50
which reported
that using a cut-off of 140/90 mmHg and gender adjustment,
25% of men and 26% of women had hypertension. Based on
BMI categories, our study showed that obese groups (35%) had
a high prevalence of hypertension when compared to the normal
(18%) and overweight groups (22%). These findings are similar
to a study by Dua
et al
.,
51
which found that the prevalence of
high BP was greater in those with high BMI. This has also been
reported in other studies.
52,53
The WHO
4
reported that hypertension
was globally responsible for 45% of deaths due to cardiovascular
disease and 51% of deaths due to stroke. According to Ibrahim
and Damasceno,
54
as well as the WHO,
4
an estimated one billion
people worldwide are hypertensive, and this number is expected to
rise to 1.56 billion by 2025.
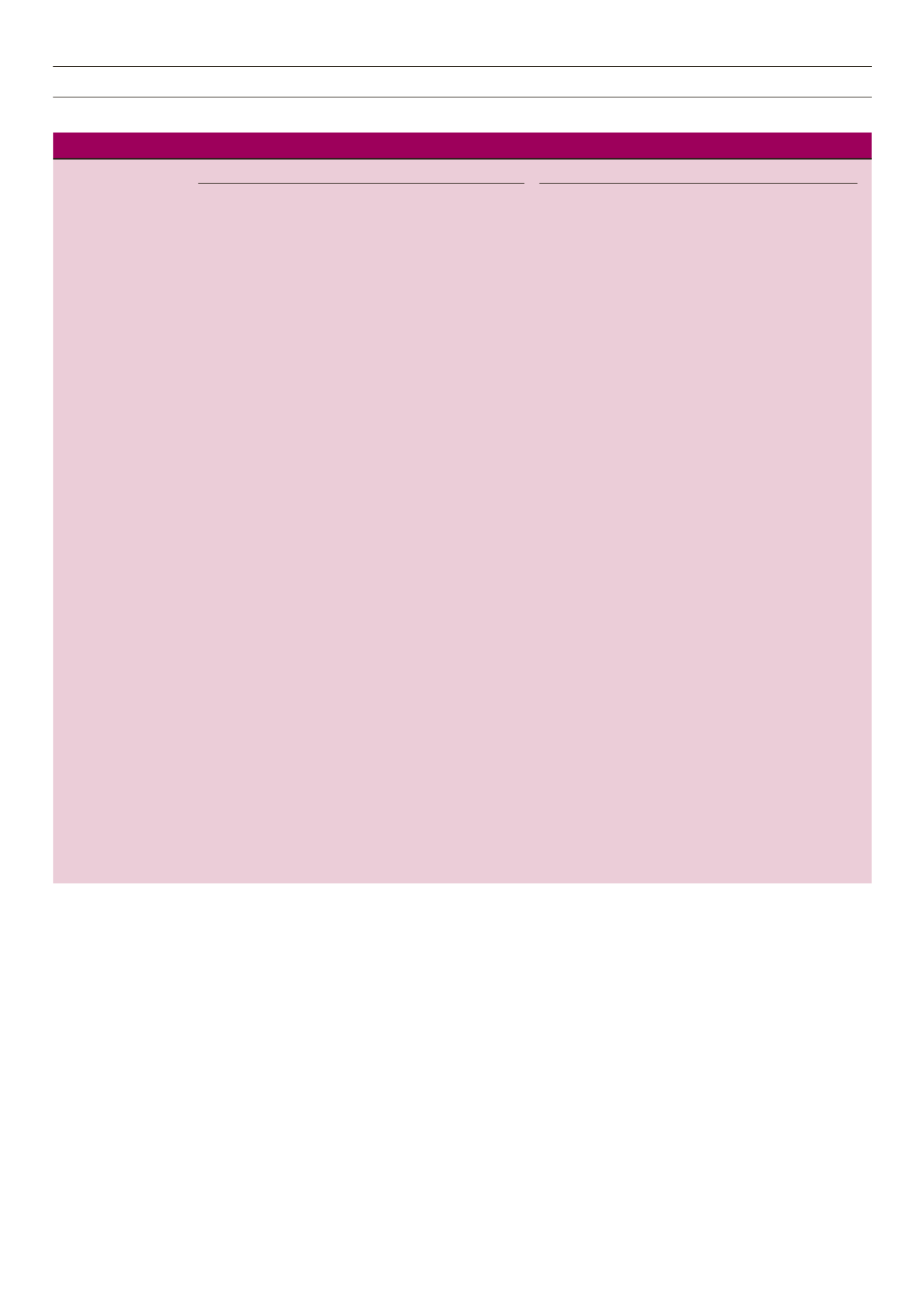
Table 3.
Participants’ anthropometric and physiological characteristics according to BMI categories by gender
Men
Women
p
-value of the
p
-value of the
Variables
n
Mean
SD
differences
n
Mean
SD differences
Height (cm)
Underweight
15
169.73
9.94
0.05
1
169.00
.
0.18
Normal
123
170.71
7.19
55
161.76
9.27
Overweight
49
170.22
7.38
72
160.01
6.26
Obese
35
165.60
17.34
118
159.46
7.31
Total
222
169.73
9.81
246
160.18
7.55
Body weight (kg)
Underweight
15
49.51
5.77
< 0.001
1
51.00
.
< 0.001
Normal
123
66.75
7.93
55
60.75
6.38
Overweight
49
81.50
7.68
72
73.38
5.93
Obese
35
95.09
14.77
118
92.19
14.63
Total
222
73.31
15.35
246
79.49
17.09
BMI (kg/m
2
)
Underweight
15
17.17
1.23
< 0.001
1
17.85
.
< 0.001
Normal
123
22.89
2.13
55
23.23
1.84
Overweight
49
28.09
1.42
72
28.65
1.46
Obese
35
34.97
5.07
118
36.20
4.87
Total
222
25.55
5.58
246
31.01
6.45
WC (cm)
Underweight
15
73.47
4.56
< 0.001
1
79.00
.
< 0.001
Normal
123
85.24
12.30
55
81.85
6.92
Overweight
49
96.53
7.13
72
92.15
12.39
Obese
35
105.81
15.70
118
105.31
14.08
Total
222
90.18
14.63
246
96.11
15.56
SBP (mmHg)
Underweight
15
138.80
27.28
0.65
1
156.00
.
< 0.001
Normal
123
142.20
23.05
55
130.31
21.17
Overweight
49
138.45
18.07
72
137.25
23.98
Obese
35
138.23
21.06
118
147.99
24.52
Total
222
140.52
21.98
246
140.93
24.63
DBP (mmHg)
Underweight
15
83.27
15.13
0.44
1
92.00
.
< 0.001
Normal
123
78.05
14.53
55
74.80
11.11
Overweight
49
80.67
10.96
72
78.30
11.43
Obese
35
79.57
10.49
118
86.48
12.63
Total
222
79.22
13.29
246
81.50
12.91
WHtR
Underweight
15
0.43
0.02
< 0.001
1
0.46
.
< 0.001
Normal
123
0.50
0.08
55
0.50
0.05
Overweight
49
0.56
0.04
72
0.57
0.07
Obese
35
0.62
0.07
118
0.65
0.08
Total
222
0.53
0.08
246
0.60
0.09
BMI = body mass index, WC = waist circumference. SBP = systolic blood pressure, DBP = diastolic blood pressure, WHtR= waist-to-height ratio, n = number, SD =
standard deviation.