VOLUME 17 NUMBER 2 • NOVEMBER 2020
59
SA JOURNAL OF DIABETES & VASCULAR DISEASE
Report
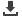
kidneys and liver (Fig. 4). Variations in weight loss potential are
seen among individual GLP-1 RAs and in different patient groups.
Liraglutide is the most potent and best researched for weight loss
in the GLP-1 class, with a 3-mg daily dose found to be beneficial as
an anti-obesity treatment in patients without diabetes (Table 2).
5,15,16
Are all GLP-1 RAs equal with regard to weight loss?
A recent comparison of dulaglutide and liraglutide in the AWARD-6
study showed a statistically significantly greater weight loss with
liraglutide (Fig. 5), with a difference of 700 g in six months.
17
However, once-weekly dulaglutide has similar glucose-lowering
efficacy as the 1.8-mg liraglutide dose and good cardiovascular
outcomes. Treatment with exenatide has been associated with only
a modest weight loss (2.49 ± 0.66 kg) in a cohort of obese non-
diabetic women.
18
Exenatide has not shown any cardiovascular
benefit.
The SUSTAIN-7 trial, a head-to-head comparison between
semaglutide and dulaglutide as add-on to metformin, demonstrated
significantly greater weight loss at 40 weeks with semaglutide. As
T2DM and lifestyle factors are the usual consequences of obesity,
clinicians should consider this treatment option in very obese
subjects not willing or able to undergo metabolic surgery.
19
SGLT-2 inhibitors
Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors (canagliflozin,
dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, ertugliflozin) reduce glucose
reabsorption by the kidneys, leading to increased urinary glucose
excretion. This may result in weight loss via direct caloric loss in
the form of glycosuria, as well as improved glucose control.
5
Major adverse effects reported are urinary tract and genital fungal
infections (from increased glucose excretion through the kidney)
that may lead to discontinuation of the drugs.
15
A beneficial class
effect is renoprotection – a more than 40% reduction of renal
disease, renal failure, renal replacement therapy and worsening
renal function on average. There is also significant benefit in heart
failure, with hospitalisation reduced by nearly 40%. Empagliflozin
data show a lowering of cardiovascular mortality by an impressive
38% (relative risk reduction) in patients with established
cardiovascular disease.
DPP-4 inhibitors
DPP-4 inhibitors are weight neutral. While use of dipeptidyl
peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors (alogliptin, linagliptin, saxagliptin,
Fig. 4.
The physiological roles of GLP-1 and therapeutic benefits of GLP-1 RAs.
15
Table 2.
Anti-obesity treatments: liraglutide and weight management
16
• Individuals without T2DM, BMI > 30 kg/m
2
or > 27 kg/m
2
in the presence
of treated or untreated dyslipidaemia or hypertension.
• 3.0 mg liraglutide injected subcutaneously vs placebo; all subjects received
counselling on lifestyle modification.
• At 56 weeks, the liraglutide group had lost a mean of 8.4 ± 7.3 kg of body
weight and the placebo group had lost a mean of 2.8 ± 6.5 kg.
• Of patients in the liraglutide group, 63.2% lost at least 5% of their
body weight compared with 27.1% in the placebo group (
p
< 0.001);
33.1 and 10.6%, respectively, lost more than 10% of their body weight
(
p
< 0.001).
• Liraglutide treatment was associated with reductions in cardiometabolic risk
factors, including waist circumference, blood pressure and inflammatory
markers, along with modest improvements in fasting lipid levels.