VOLUME 17 NUMBER 2 • NOVEMBER 2020
57
SA JOURNAL OF DIABETES & VASCULAR DISEASE
Report
Independent of the population-specific BMI thresholds determining
overweight and obesity, visceral fat distribution has been found to
elevate the risk of mortality.
1
What are the benefits of weight loss in diabetes
prevention and therapy?
The progression of T2DM can be arrested and often reversed in the
first five years after diagnosis by significantly reducing body weight
(≥ 10%); the metabolic dysregulation and inflammatory processes
that predispose to T2DM can frequently be corrected.
5
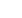
The Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study
7
showed that in pre-
diabetic individuals, intensive dietary and exercise programmes
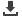
Fig. 1.
Pathways from obesity to diabetes.
6
decreased the overall risk of diabetes by 58% (Fig. 2). Similarly,
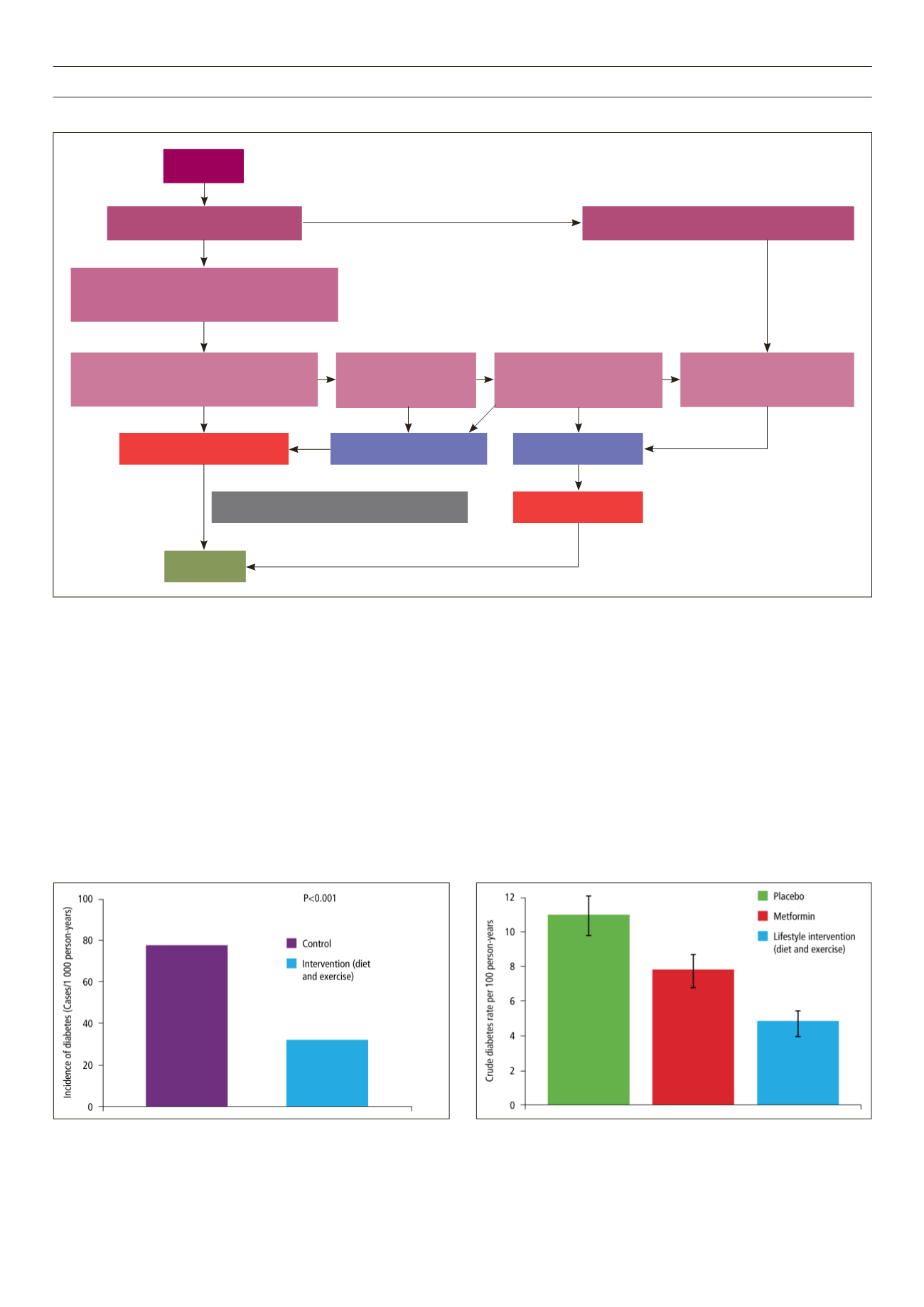
the Diabetes Prevention Program
8
showed that moderate weight
loss with lifestyle intervention in an obese population with
impaired glucose tolerance could reduce the incidence of diabetes
by 58%, whereas metformin alone reduced diabetes incidence
by only 31% (Fig. 3).
The American Cancer Society’s Cancer Prevention Study I
indicated that intentional weight loss of 10 kg in those with T2DM
reduced total mortality by approximately 25%. Other clinical
trials have demonstrated that a loss of 5–10% of body weight
in diabetes patients demonstrates beneficial effects at one year
(Table 1).
9-12
Fig. 2.
Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study: intensive dietary and exercise
intervention decreases overall risk of diabetes.
Fig. 3.
Diabetes Prevention Programme: lifestyle modification is superior to
metformin for the prevention of T2DM.
Obesity
Permanent elevation of FFA
Inhibits glucose transport activity
Predominant utilisation of lipids by muscle
Accumulation of TG in liver and beta-cells
i
Glucose uptake by muscle
i
Glycogen synthesis in skeletal muscle
i
INSULIN RESISTANCE
DIABETES
INSULIN DEFICIENCY
i
Insulin secretion
Impairs insulin sensitivity
Oxidative stress and systemic inflammation
Hepatic and islet dysfunction
(lipotoxicity)
h
Insulin secretion
(sustained hyperinsulinaemia)
Chronic hyperglycaemia
(glucotoxicity)