RESEARCH ARTICLE
SA JOURNAL OF DIABETES & VASCULAR DISEASE
64
VOLUME 13 NUMBER 2 • DECEMBER 2016
reperfusion and culminating in the formation of an infarct has been
ascribed, among others, to the activity of the phosphatidylinositol-
3-kinase (PI-3K) pathway. In view of the previously reported
improvements in insulin sensitivity of cardiomyocytes, induced by
P glandulosa
treatment,
8
we systematically analysed the proteins
involved in this signalling cascade.
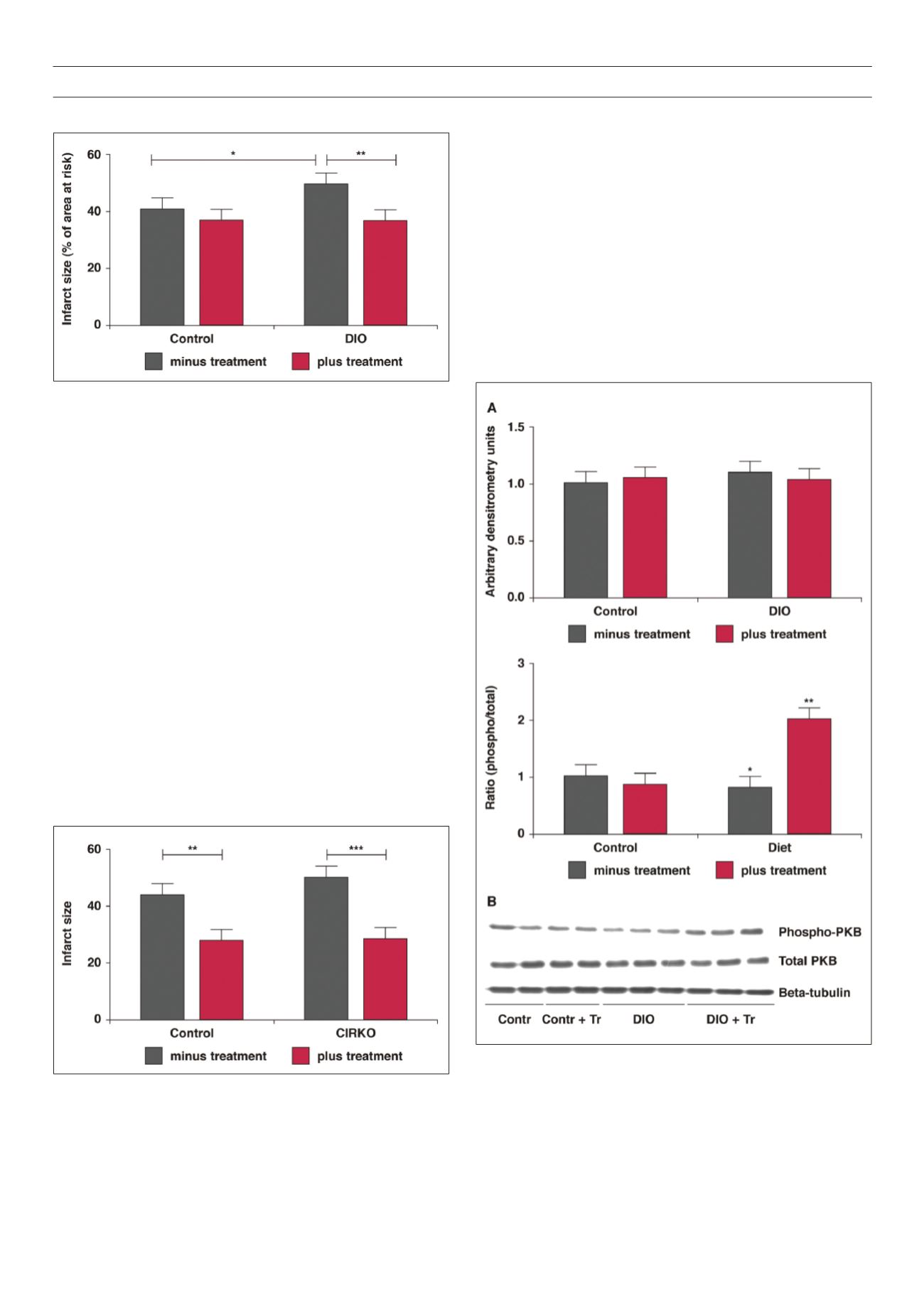
As summarised in Table 2 and shown in Fig. 4, hearts from the DIO
animals presented with a significantly lower phosphorylated:total
ratio of the central protein in this cascade, protein kinase B or Akt.
This ratio was significantly improved by treatment. In addition, the
expression of the p85 regulatory subunit of the PI-3K enzyme was
significantly lower in hearts from the DIO animals, whereas this was
not the case after treatment.
Treatment also resulted in a lower expression of the phosphatase
and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN)
with a higher state of phosphorylation of this enzyme (Fig. 5).
Phosphorylation of PTEN further inactivates this enzyme, responsible
also for the dephosphorylation of PKB/Akt.
17,18
Fig. 2.
After the 16-week diet plus P glandulosa treatment, isolated hearts from
DIO rats were perfused ex vivo in the working-heart mode. They were subjected
to regional ischaemia as described in Methods. Infarct size was determined as a
percentage of the area at risk of infarction. *
p
< 0.05, **
p
< 0.01,
n
= 15–17
per group.
Fig. 3.
After the eight weeks of treatment, hearts were removed from the CIRKO
mice and perfused ex vivo in the Langendorff mode and subjected to NICA as
described in Methods. Infarct size was determined throughout the whole heart
and expressed as a percentage of the total surface. **
p
< 0.01, ***
p
< 0.001,
n
= 9 per group.
Fig. 4.
Hearts from the treated and untreated DIO animals were removed without
any intervention and stored in liquid nitrogen. Tissue lysates were prepared and
Western blotting was performed as described in Methods.
A
: bar charts of the
expression of PKB protein as well as the ratio of phosphorylated vs total protein.
*
p
< 0.05 vs control; **
p
< 0.01 vs untreated DIO,
n
= 6 individual hearts
analysed per group.
B
is a representative blot depicting these proteins and beta-
tubulin, used as an indicator of equal loading.
Anti-hypertensive effects
As the DIO diet does not cause high blood pressure, we used a
modification of a high-fat diet to induce hypertension in the
animals.
12
As can be seen in Fig. 5, these animals developed a
significant elevation of their blood pressure within four weeks (HFD
135.88 ± 2.0 vs control 125.85 ± 1.9 mmHg,
p
< 0.05,
n
= 8 per
group).
We either pre-treated the animals with
P glandulosa
, starting
at the onset of the diet, or we allowed the animals to become
severely hypertensive (12 weeks) and then started the treatment.
We included a group of animals treated with the angiotensin
converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor captopril from the onset of the
diet, as a positive control in this study.